Published:
How do USound MEMS speakers work?
USound was the first company to introduce MEMS speakers on the audio market. This article explains how our MEMS speakers work, enabling manufacturers to create highly advanced and customizable audio systems.
Piezoelectricity & USound’s MEMS speakers
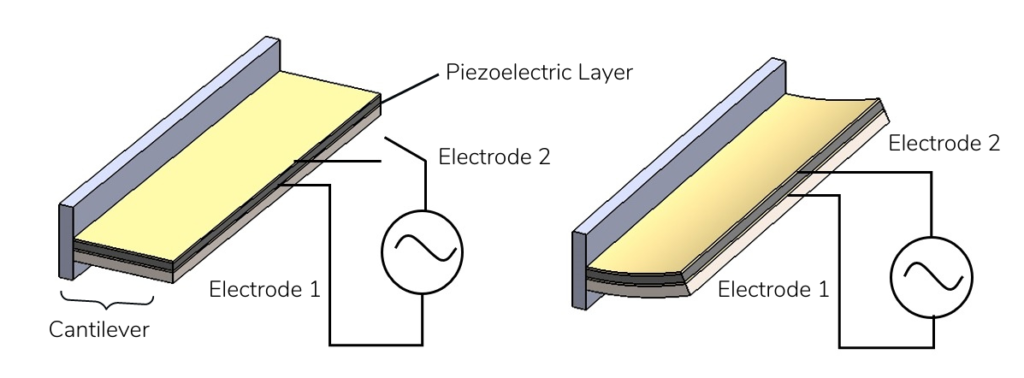
USound’s MEMS speakers are based on the piezoelectric effect. Piezoelectricity is the process of using crystals to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, or vice versa. Crystals with these properties are for example aluminium nitride (AlN) or lead zirconate titanate (PZT). These materials expand or shrink in an electric field.
In a practical configuration, such an electric field is generated between electrodes and applied to a piezoelectric layer. This layer is put on top of a substrate (for example a silicon plate). If an electric field is applied across its electrodes, the top layer contracts and bends both layers upwards.
The bending movement of the cantilever in the MEMS loudspeaker is transformed into a one-dimensional piston-like motion to effectively drive the loudspeaker membrane. In order to achieve this piston-like movement, a spring structure incorporates multiple bending cantilevers that are connected to a central element. By arranging the cantilevers symmetrically, the central element exclusively moves in an up-and-down manner.
To produce sound, it is necessary to displace air. Enhancing the air displacement, the compact MEMS structure is linked to a membrane that amplifies the motion over a larger surface area. Consequently, the result is an efficient system with higher efficacy compared to a conventional electrodynamic speaker. Rather than relying on a bulky magnet-coil actuator, the USound MEMS speaker utilizes integrated piezo-actuators on a MEMS chip to propel the membrane and generate sound.
Create the most advanced audio systems for hearables and wearables with USound’s MEMS speakers. Contact our sales department and learn more.

